- 2002, Glucosamine/Chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial Primary Study National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Towheed T et al, 2009, Glucosamine for osteoarthritis Cochrane Summaries
- Glucosamine Drugs.com
- Glucosamine ChemSpider
- Knudsen JF, 2008, Potential glucosamine-warfarin interaction resulting in increased international normalized ratio: case report and review of the literature and MedWatch database PubMed
- Simon RR et al, 2011, A comprehensive review of oral glucosamine use and effects on glucose metabolism in normal and diabetic individuals PubMed Central
- Sugars and Polysaccharides Southern Illinois University
- Does glucosamine raise “bad” LDL cholesterol? ConsumerLab
Glucosamine
What is glucosamine?
Glucosamine is an amino sugar made from chitin, which is extracted from the shellfish shells.
It also occurs in small amounts in certain foods and in the human body ─ in the cartilage and in the fluid that surrounds the joints.
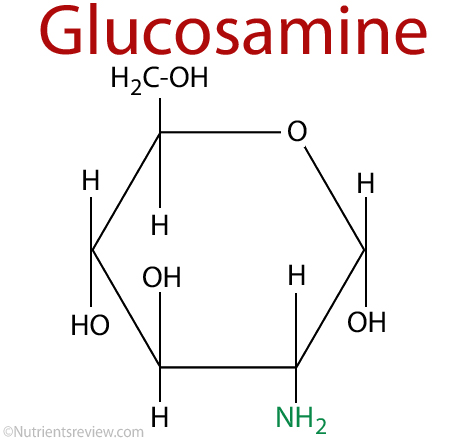
Chemical Formula
Chemical formula of glucosamine is C6H13NO5 [4]. Glucosamine is a monosaccharide, so it is a carbohydrate [7].
Picture 1. Glucosamine chemical formula
What is glucosamine used for?
Glucosamine is used to treat joint pain, mainly knee pain due to osteoarthritis (cartilage damage in joints due to wear and tear) but also for hip and back pain, tendonitis, gout, glaucoma, wound healing and hair growth. Long distance runners often use it.
Glucosamine Supplements
Types
- Glucosamine
- Glucosamine sulfate
- Glucosamine chondroitin sulfate
- Glucosamine hydrochloride
- N-acetyl-glucosamine
- Glucoamine MSM (Methyl SulfonylMethane)
Forms. Glucosamine is available as tablets, capsules, chewables, powder, liquid for oral use and as lotion for topical use (to apply on the skin).
In Europe, glucosamine is sold as a drug and in the United States as an over-the-counter (OTC) dietary supplement [2].
Does glucosamine work?
There is INSUFFICIENT EVIDENCE about effectiveness of glucosamine in relieving joint pain caused by osteoarthritis.
- In one 2009 Cochrane review of high quality studies, glucosamine was no more effective than placebo [2].
- In the GAIT study in the U.S. in 2002, glucosamine tablets (3 x 500 mg/day) in combination with chondroitin sulfate tablets (3 x 400 mg/day) reduced pain (after 6 months of taking) in some individuals with moderate to severe knee pain but not in those with mild pain [1]. After 24 months of taking, X-ray studies of the knees did not reveal any benefit for cartilage over placebo, though.
There is also insufficient evidence about glucosamine effectiveness in weight loss and treatment temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain and glaucoma.
Usual Dosage
Tablets: 1500 mg in one dose or 3 x 500 mg/day [2]
Safety
Glucosamine is likely safe to use.
Glucosamine does not likely affect blood glucose levels in healthy individuals and those with diabetes mellitus [6].
During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Do not take glucosamine if you are pregnant or you are breastfeeding. The safety of glucosamine during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not known due to insufficient studies [3].
Side Effects
Side effects after glucosamine pills are rare and may include stomach upset, heartburn, nausea, diarrhea or constipation [3].
Individuals with a shellfish allergy are typically allergic to shellfish meat and not shells, from which glucosamine is extracted.
Glucosamine sulfate does not likely raise blood cholesterol levels [8].
Glucosamine-Drug Interactions
Glucosamine taken along with warfarin (a blood thinner) may increase the effectiveness of warfarin and thus increase the risk of bleeding but more research is warranted [5].
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is glucosamine vegan?
Glucosamine is usually produced from the shellfish shells, but synthetically produced from wheat or corn, and therefore vegan, supplements are available.
2. What ingredients glucosamine supplements contain?
Besides glucosamine, supplements may contain shark cartilage and chondroitin.
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions